Shell Commands
This sketch demonstrates running Linux shell commands on a Yún device.
It runs the wifiCheck script (located at /usr/bin/pretty-wifi-info.lua) on the Linux processor, then uses grep to get the signal strength.
On the board, parseInt() is called to read the WiFi signal strength as an integer, and uses that number to fade an LED with analogWrite().
Hardware Required
Yún board or shield
Yún device connected to a wireless network
220 ohm resistor
LED
hook-up wires
breadboard
Circuit
A red LED connected to digital pin 9 through a 220 ohm resistor on the breadboard.

image developed using Fritzing. For more circuit examples, see the Fritzing project page
Schematic
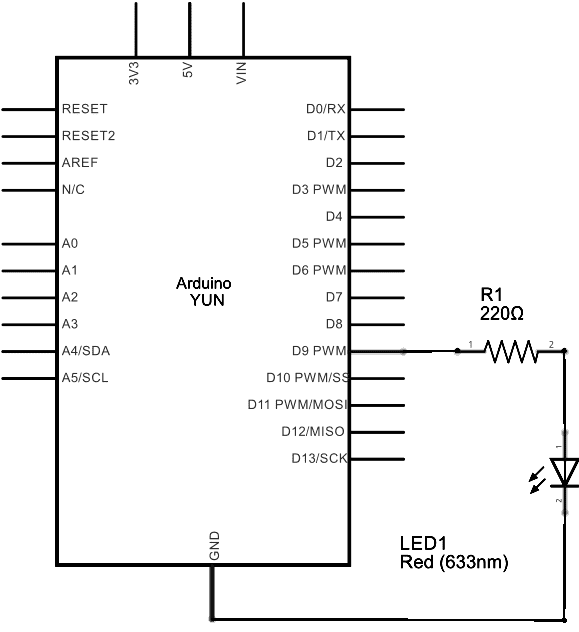
image developed using Fritzing. For more circuit examples, see the Fritzing project page
Code
Include the Process class in your sketch.
#include <Process.h>
In setup(), you'll want to initialize Bridge and start a serial connection. Before running the rest of the sketch, wait for a serial connection to become active.
void setup() {
Bridge.begin();
Serial.begin(9600);
while (!Serial);
}Create a named Process with which you'll use to run the WiFi status script and grep.
void loop() {
Process p;Pass runShellCommand() the path of the script you wish to run, along with any additional commands. In this case, you'll call "grep Signal" to pull out just the signal strength of the WiFi connection.
p.runShellCommand("/usr/bin/pretty-wifi-info.lua | grep Signal");
Wait until the process finishes so you get the entire output
while(p.running());
Once the process has finished running, use parseInt() to look for an integer that represents the signal strength. It should be in the range of 0 - 100. Map the result to a value between 0 and 255 with map() and use that value to adjust the brightness of the LED on pin 9 with analogWrite(). Print the signal strength to the serial monitor and wait for a few seconds before starting again.
while (p.available()) {
int result = p.parseInt();
int signal = map(result, 0, 100, 0, 255);
analogWrite(9, signal);
Serial.println(result);
}
delay(5000);
}The LED should change its brightness as the WiFi signal strength fluctuates.
The complete sketch is below:
/*
Running shell commands using Process class.
This sketch demonstrate how to run linux shell commands
using a YunShield/Yún. It runs the wifiCheck script on the Linux side
of the Yún, then uses grep to get just the signal strength line.
Then it uses parseInt() to read the wifi signal strength as an integer,
and finally uses that number to fade an LED using analogWrite().
The circuit:
* YunShield/Yún with LED connected to pin 9
created 12 Jun 2013
by Cristian Maglie
modified 25 June 2013
by Tom Igoe
This example code is in the public domain.
http://www.arduino.cc/en/Tutorial/ShellCommands
*/
#include <Process.h>
void setup() {
Bridge.begin(); // Initialize the Bridge
SerialUSB.begin(9600); // Initialize the Serial
// Wait until a Serial Monitor is connected.
while (!SerialUSB);
}
void loop() {
Process p;
// This command line runs the WifiStatus script, (/usr/bin/pretty-wifi-info.lua), then
// sends the result to the grep command to look for a line containing the word
// "Signal:" the result is passed to this sketch:
p.runShellCommand("/usr/bin/pretty-wifi-info.lua | grep Signal");
// do nothing until the process finishes, so you get the whole output:
while (p.running());
// Read command output. runShellCommand() should have passed "Signal: xx&":
while (p.available()) {
int result = p.parseInt(); // look for an integer
int signal = map(result, 0, 100, 0, 255); // map result from 0-100 range to 0-255
analogWrite(9, signal); // set the brightness of LED on pin 9
SerialUSB.println(result); // print the number as well
}
delay(5000); // wait 5 seconds before you do it again
}See Also
Bridge Library - Your reference to the Bridge Library
Bridge - Simple REST style calls to access analog and digital pins
Console Ascii Table - A complete ASCII table printed to the Console
Console Pixel - Turn an LED on and off through the Console
Console Read - Read data coming from bridge using the Console.read() function
Data Logger - Log data from three analog sensors to an SD card.
File Write - How to write file into the Yún filesystem.
Http Client - A basic HTTP client that connects to the internet and downloads content.
Http Client Console - HTTP client that connects, downloads content and shows it using WiFi and Console.
Mailbox Read Message - How to read the messages queue, called Mailbox, using the Bridge library.
Process - How to run linux processes using an Yún.
Remote Due Blink - How to upload remotely a sketch on DUE boards.
Temperature Web Panel - How to serve data from an analog input via the Yún's built-in webserver.
Time check - Gets the time from Linux via Bridge then parses out hours, minutes and seconds.
WiFi Status - Prints information about the status of your wifi connection.
Yún First Configuration - Easily configure your Yún device using Serial Monitor and USB port.
Serial Terminal - Use the Yún's 32U4 processor as a serial terminal for the Linux side on the Yún.
Last revision 2016/05/25 by SM