Smoothing
This sketch reads repeatedly from an analog input, calculating a running average and printing it to the computer. This example is useful for smoothing out the values from jumpy or erratic sensors, and also demonstrates the use of arrays to store data.
Hardware
Arduino Board
10k ohm potentiometer
Circuit
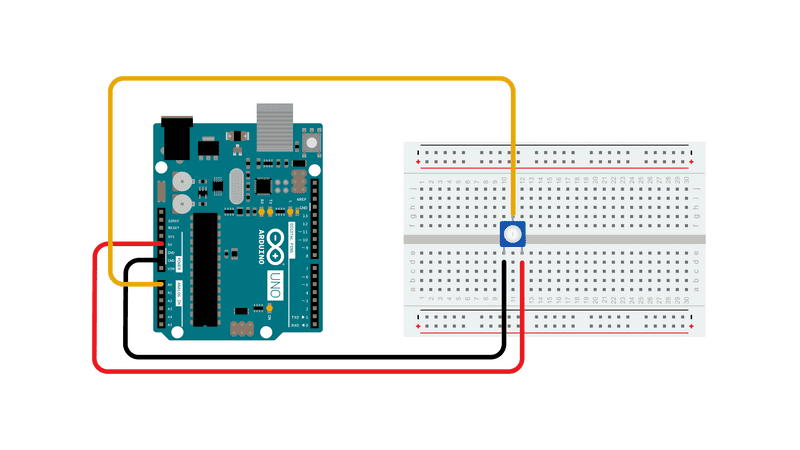
Connect one pin of a potentiometer to 5V, the center pin to analog pin 0, and the the last pin to ground.
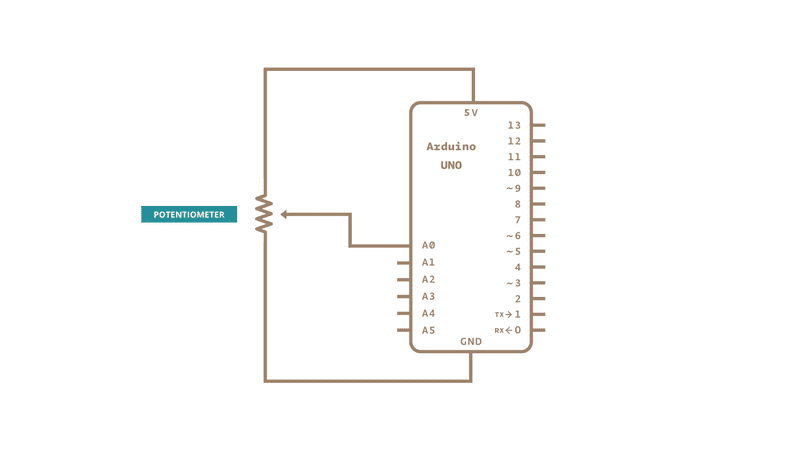
Schematic
Code
The code below sequentially stores 10 readings from your analog sensor into an arrays, one by one. With each new value, the sum of all the numbers is generated and divided, producing an average value which then be used to smooth outlying data. Because this averaging takes place each time a new value is added to the array (rather then waiting for 10 new values, for instance) there is no lag time in calculating this running average.
Altering the size of the array used, by changing numReadings to a larger value will smooth the data collected even further.
See Also:
AnalogInOutSerial - Read an analog input pin, map the result, and then use that data to dim or brighten an LED.
AnalogInput - Use a potentiometer to control the blinking of an LED.
AnalogWriteMega - Fade 12 LEDs on and o¬ff, one by one, using an Arduino Mega board.
Calibration - Define a maximum and minimum for expected analog sensor values.
Fading - Use an analog output (PWM pin) to fade an LED.
Last revision 2015/07/29 by SM