Fading
This example demonstrates the use of analog output (Pulse Width Modulation (PWM)) to fade an LED. PWM is a technique for getting an analog-like behavior from a digital output by switching it off and on very fast and with different ratio between on and off time.
Hardware Required
Arduino board
LED
220 ohm resistor
hook-up wires
breadboard
Circuit
An LED connected to digital output pin 9 through a 220 ohm resistor.
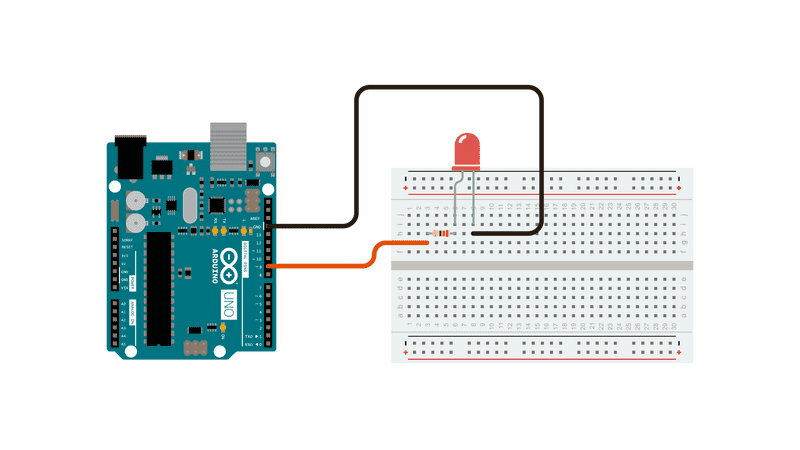
Schematic
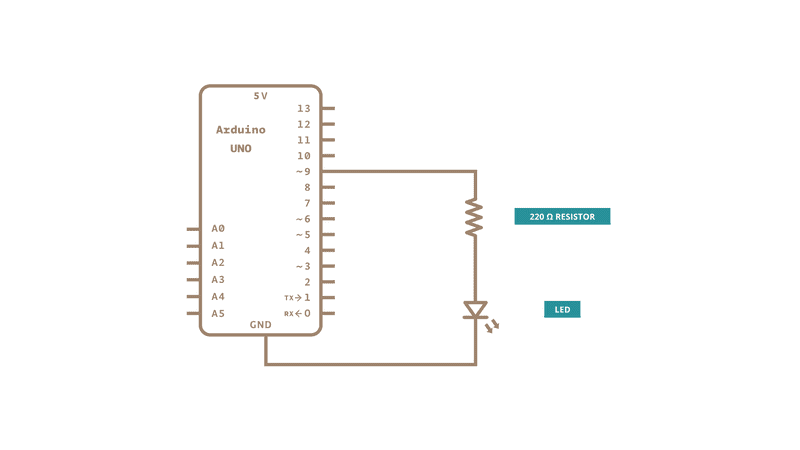
Code
In this example two loops are executed one after the other to increase and then decrease the value of the output on pin 9.
/*
Fading
This example shows how to fade an LED using the analogWrite() function.
The circuit:
- LED attached from digital pin 9 to ground.
created 1 Nov 2008
by David A. Mellis
modified 30 Aug 2011
by Tom Igoe
This example code is in the public domain.
http://www.arduino.cc/en/Tutorial/Fading
*/
int ledPin = 9; // LED connected to digital pin 9
void setup() {
// nothing happens in setup
}
void loop() {
// fade in from min to max in increments of 5 points:
for (int fadeValue = 0 ; fadeValue <= 255; fadeValue += 5) {
// sets the value (range from 0 to 255):
analogWrite(ledPin, fadeValue);
// wait for 30 milliseconds to see the dimming effect
delay(30);
}
// fade out from max to min in increments of 5 points:
for (int fadeValue = 255 ; fadeValue >= 0; fadeValue -= 5) {
// sets the value (range from 0 to 255):
analogWrite(ledPin, fadeValue);
// wait for 30 milliseconds to see the dimming effect
delay(30);
}
}See Also:
for()
delay()
AnalogInOutSerial - Read an analog input pin, map the result, and then use that data to dim or brighten an LED.
AnalogInput - Use a potentiometer to control the blinking of an LED.
AnalogWriteMega - Fade 12 LEDs on and o¬ff, one by one, using an Arduino Mega board.
Calibration - Define a maximum and minimum for expected analog sensor values.
Smoothing - Smooth multiple readings of an analog input.
Last revision 2015/07/29 by SM