If Statement (Conditional Statement)
The if() statement is the most basic of all programming control structures. It allows you to make something happen or not, depending on whether a given condition is true or not. It looks like this:
if (someCondition) {
// do stuff if the condition is true
}There is a common variation called if-else that looks like this:
if (someCondition) {
// do stuff if the condition is true
} else {
// do stuff if the condition is false
}There's also the else-if, where you can check a second condition if the first is false:
if (someCondition) {
// do stuff if the condition is true
} else if (anotherCondition) {
// do stuff only if the first condition is false
// and the second condition is true
}You'll use if statements all the time. The example below turns on an LED on pin 13 (the built-in LED on many Arduino boards) if the value read on an analog input goes above a certain threshold.
Hardware Required
Arduino Board
Potentiometer or variable resistor
Circuit
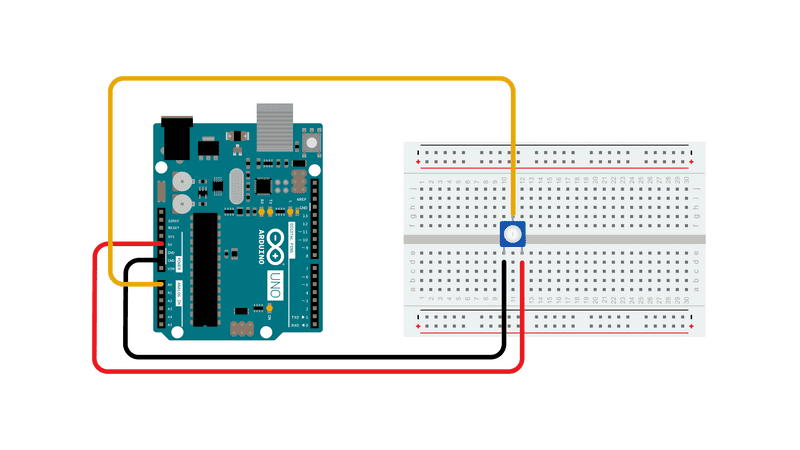
Schematic
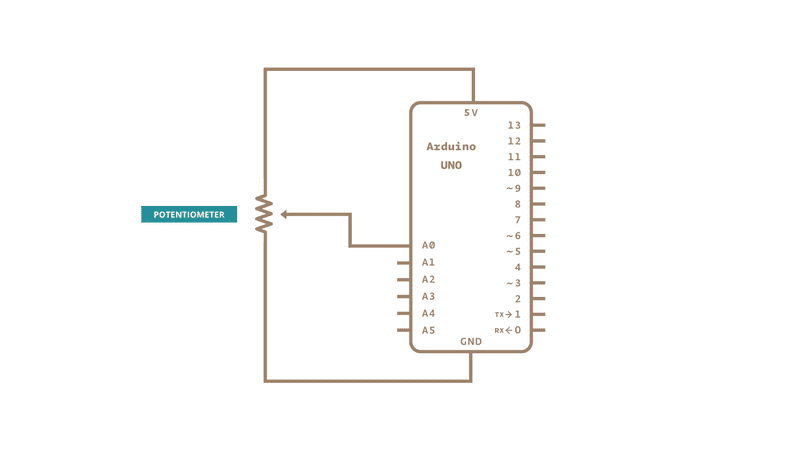
Code
In the code below, a variable called analogValue is used to store the data collected from a potentiometer connected to the board on analogPin 0. This data is then compared to a threshold value. If the analog value is found to be above the set threshold the built-in LED connected to digital pin 13 is turned on. If analogValue is found to be < (less than) threshold, the LED remains off.
See Also
if()
Arrays - A variation on the For Loop example that demonstrates how to use an array.
ForLoopIteration - Control multiple LEDs with a for loop.
switchCase - How to choose between a discrete number of values.
switchCase2 - A second switch-case example, showing how to take different actions based on the characters received in the serial port.
WhileStatementConditional - How to use a while loop to calibrate a sensor while a button is being read.
Last revision 2015/07/29 by SM