While Loop
Sometimes you want everything in the program to stop while a given condition is true. You can do this using a while loop. This example shows how to use a while loop to calibrate the value of an analog sensor.
In the main loop, the sketch below reads the value of a photoresistor on analog pin 0 and uses it to fade an LED on pin 9. But while a button attached to digital pin 2 is pressed, the program runs a method called calibrate() that looks for the highest and lowest values of the analog sensor. When you release the button, the sketch continues with the main loop.
This technique lets you update the maximum and minimum values for the photoresistor when the lighting conditions change.
Hardware Required
Arduino Board
pushbutton or switch
photoresistor or another analog sensor
2 10k ohm resistors
breadboard
Circuit
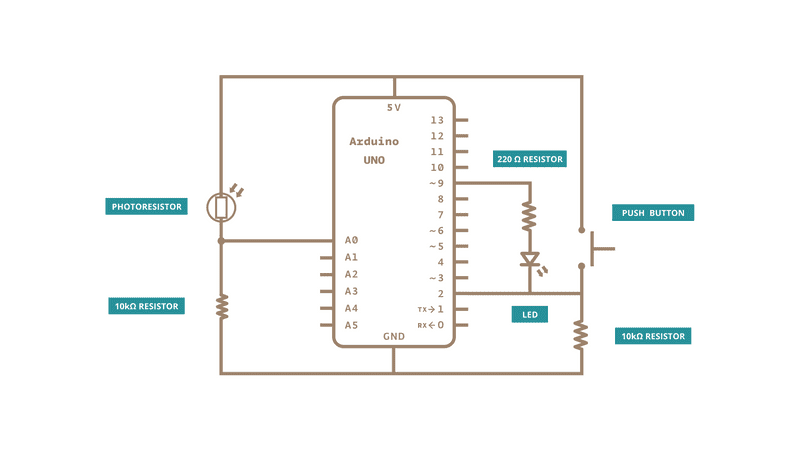
Connect your analog sensor (e.g. potentiometer, light sensor) on analog input 2 with a 10K ohm resistor to ground. Connect your button to digital pin, again with a 10K ohm resistor to ground. Connect your LED to digital pin 9, with a 220 ohm resistor in series.
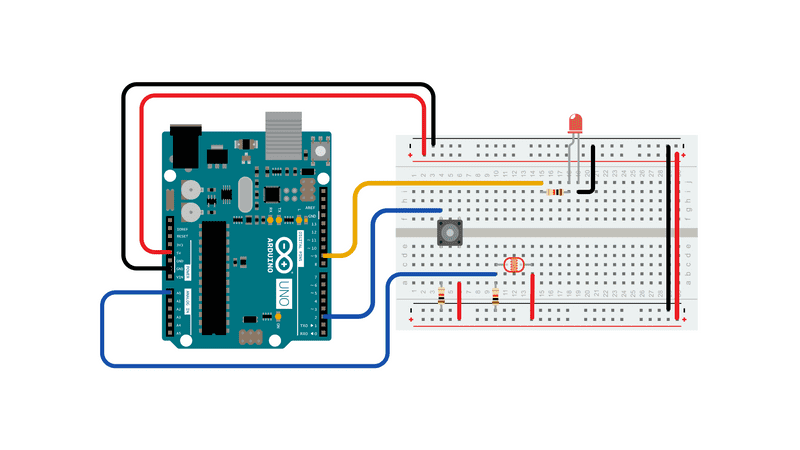
Schematic
Code
/*
Conditionals - while statement
This example demonstrates the use of while() statements.
While the pushbutton is pressed, the sketch runs the calibration routine.
The sensor readings during the while loop define the minimum and maximum of
expected values from the photoresistor.
This is a variation on the calibrate example.
The circuit:
- photoresistor connected from +5V to analog in pin 0
- 10 kilohm resistor connected from ground to analog in pin 0
- LED connected from digital pin 9 to ground through 220 ohm resistor
- pushbutton attached from pin 2 to +5V
- 10 kilohm resistor attached from pin 2 to ground
created 17 Jan 2009
modified 30 Aug 2011
by Tom Igoe
modified 20 Jan 2017
by Arturo Guadalupi
This example code is in the public domain.
http://www.arduino.cc/en/Tutorial/WhileLoop
*/
// These constants won't change:
const int sensorPin = A0; // pin that the sensor is attached to
const int ledPin = 9; // pin that the LED is attached to
const int indicatorLedPin = 13; // pin that the built-in LED is attached to
const int buttonPin = 2; // pin that the button is attached to
// These variables will change:
int sensorMin = 1023; // minimum sensor value
int sensorMax = 0; // maximum sensor value
int sensorValue = 0; // the sensor value
void setup() {
// set the LED pins as outputs and the switch pin as input:
pinMode(indicatorLedPin, OUTPUT);
pinMode(ledPin, OUTPUT);
pinMode(buttonPin, INPUT);
}
void loop() {
// while the button is pressed, take calibration readings:
while (digitalRead(buttonPin) == HIGH) {
calibrate();
}
// signal the end of the calibration period
digitalWrite(indicatorLedPin, LOW);
// read the sensor:
sensorValue = analogRead(sensorPin);
// apply the calibration to the sensor reading
sensorValue = map(sensorValue, sensorMin, sensorMax, 0, 255);
// in case the sensor value is outside the range seen during calibration
sensorValue = constrain(sensorValue, 0, 255);
// fade the LED using the calibrated value:
analogWrite(ledPin, sensorValue);
}
void calibrate() {
// turn on the indicator LED to indicate that calibration is happening:
digitalWrite(indicatorLedPin, HIGH);
// read the sensor:
sensorValue = analogRead(sensorPin);
// record the maximum sensor value
if (sensorValue > sensorMax) {
sensorMax = sensorValue;
}
// record the minimum sensor value
if (sensorValue < sensorMin) {
sensorMin = sensorValue;
}
}See Also:
while()
map()
if()
Arrays - A variation on the For Loop example that demonstrates how to use an array.
ForLoopIteration - Control multiple LEDs with a for loop.
IfStatementConditional - Use an ‘if statement' to change the output conditions based on changing the input conditions.
switchCase - How to choose between a discrete number of values.
switchCase2 - A second switch-case example, showing how to take different actions based on the characters received in the serial port.
Last revision 2015/08/11 by SM