Debounce
Tutorials > Examples > Digital > Debounce
Pushbuttons often generate spurious open/close transitions when pressed, due to mechanical and physical issues: these transitions may be read as multiple presses in a very short time fooling the program. This example demonstrates how to debounce an input, which means checking twice in a short period of time to make sure the pushbutton is definitely pressed. Without debouncing, pressing the button once may cause unpredictable results. This sketch uses the millis() function to keep track of the time passed since the button was pressed.
Hardware Required
Arduino Board
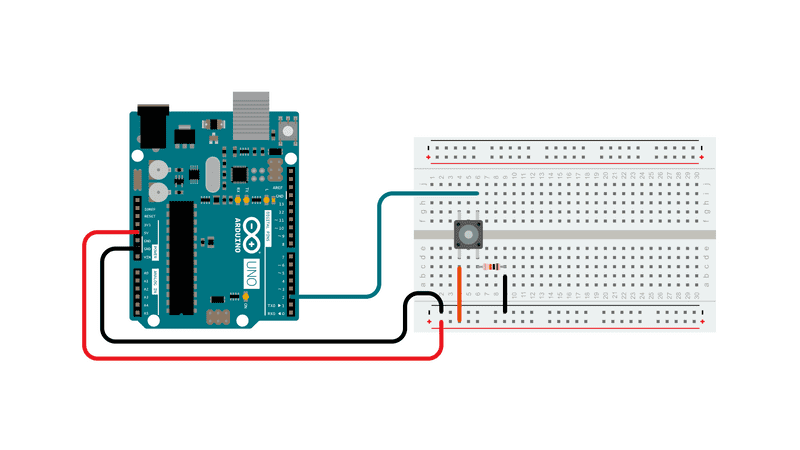
momentary button or switch
10k ohm resistor
hook-up wires
breadboard
Circuit
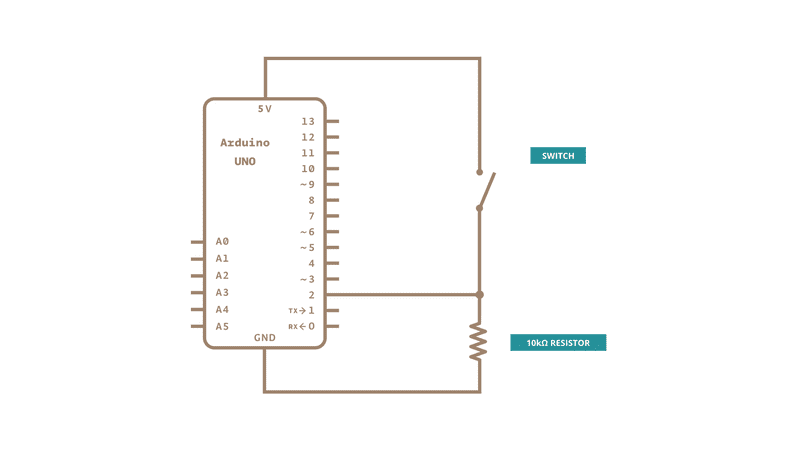
Schematic
Code
The sketch below is based on Limor Fried's version of debounce, but the logic is inverted from her example. In her example, the switch returns LOW when closed, and HIGH when open. Here, the switch returns HIGH when pressed and LOW when not pressed.
See Also
pinMode()
if()
millis()
DigitalReadSerial - read a switch, print the state out to the Serial Monitor
Blink - turn an LED on and off
Button State Change - counting the number of button pushes
Last revision 2015/07/29 by SM